The role of glutamic acid residue in proteins is of keen interest in biochemistry. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in protein chemistry, states, “Glutamic acid residues are essential for maintaining protein stability.” This highlights the importance of this amino acid in biological systems.
glutamic acid residues contribute to protein folding, structure, and function. They often participate in hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions, which stabilize proteins. Without these residues, proteins could misfold and lose functionality, leading to cellular dysfunction.
However, the benefits of glutamic acid residues are not without challenges. Overabundance can lead to unwanted aggregation. This aspect requires careful consideration in protein engineering. Understanding the nuances of glutamic acid residues may help optimize protein designs for therapeutic applications. Balancing these residues is crucial for achieving desired protein characteristics.
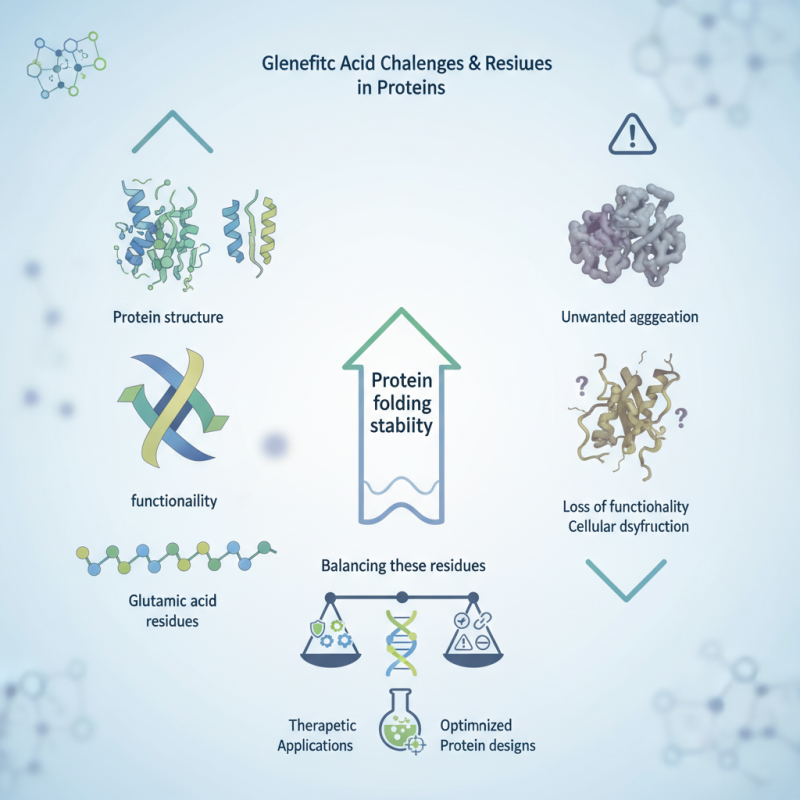
Glutamic acid residues play a crucial role in protein structure stability. These amino acids can form hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions. These interactions are vital for maintaining the three-dimensional shape of proteins. Research shows that proteins with higher glutamic acid content exhibit enhanced stability under various environmental conditions.
Studies indicate that glutamic acid contributes significantly to the polymorphism of proteins. A report revealed that proteins with a notable presence of glutamic acid can withstand changes in pH. They also perform better under stress conditions, such as increased temperature. For instance, enzymes with more glutamic acid residues maintained activity at higher temperatures compared to those with less.
However, not every protein benefits equally from glutamic acid residues. In some cases, excessive amounts can lead to instability. It creates an imbalance that disrupts the folding process. The key lies in the appropriate balance of glutamic acid in protein design. Striking this balance remains a challenge that researchers are continually exploring. Insights from structural biology are essential for future advancements in protein engineering.
This chart illustrates the various benefits of glutamic acid residues in protein structure stability, highlighting factors such as hydrogen bonding capacity, ionic interactions, and overall protein stability.
Glutamic acid, an amino acid, plays a vital role in protein function. It enhances protein structure and stability. This residue is present in many proteins, influencing their activity. The carboxylic acid group of glutamic acid can form hydrogen bonds. This interaction stabilizes protein folding.
Moreover, glutamic acid residues can act as proton donors. This ability helps in enzymatic reactions, making proteins more efficient. In certain enzymes, they are crucial for catalysis. Proteins with more glutamic acid may show improved interactions with substrates. However, an excess of this residue might lead to unwanted effects, potentially destabilizing protein structures.
Glutamic acid's role is essential but complex. It boosts performance but can also invite challenges. Understanding this balance is key in protein engineering. Researchers must consider this while designing proteins for stability and activity. Overlooking this detail could result in diminished functionality. A careful approach is crucial when manipulating glutamic acid levels in proteins.
| Benefit | Description | Role in Protein Function | Impact on Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ion Binding | Glutamic acid can bind positively charged ions, such as calcium and potassium, aiding in enzymatic reactions. | Contributes to structural stability and function of enzymes. | Enhances enzyme activity by stabilizing active sites. |
| Protein Folding | Glutamic acid participates in the folding of proteins, influencing their overall structure. | Aids in the proper conformational arrangement of polypeptides. | Improves functionality and efficiency of proteins. |
| Dynamic Interaction | Acts as a site for post-translational modifications like phosphorylation. | Regulates protein activities and interactions with other biomolecules. | Modulates signaling pathways influencing various cellular processes. |
| pH Regulation | Contributes to the maintenance of pH levels in various cellular environments. | Acts as a buffer in physiological conditions. | Boosts metabolic processes that depend on optimal pH. |
| Neurotransmission | Involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, playing a crucial role in nerve signaling. | Facilitates communication between nerve cells. | Enhances cognitive functions and neural response times. |
Glutamic acid plays a crucial role in enzyme catalysis and metabolism. This amino acid acts as a key player in various biochemical processes. It often serves as a neurotransmitter, influencing signal transmission in the brain. Enzymes depend on glutamic acid residues for proper folding and functionality.
One important aspect is its involvement in energy production. Glutamic acid helps transport nitrogen within cells. This process is vital for synthesizing amino acids and nucleotides. Without adequate glutamic acid, metabolic processes slow down. This can affect overall cellular function.
Tips: Ensure a balanced diet. Foods rich in glutamic acid, like spinach and tomatoes, support metabolic health. However, consider your overall amino acid intake. Too much or too little can disrupt the balance. Reflect on your personal nutritional needs regularly.
Glutamic acid's role in proteins extends to its impact on enzyme activity. Sometimes, the connection isn't straightforward. Factors like pH and temperature can affect enzyme performance. Thus, understanding this intricacy is essential for optimizing metabolic pathways. Consider how these variables might impact your body's processes.
Glutamic acid is a vital amino acid found in proteins. Its residue plays a crucial role in maintaining protein structure. This residue interacts with other amino acids, influencing the protein's stability and function. Through ionic bonds, glutamic acid can attract positively charged residues, creating a strong framework. These interactions help maintain the shape of proteins, which is essential for their biological roles.
Moreover, glutamic acid can affect enzymatic reactions. It often acts as an active site in enzymes, facilitating catalysis. The presence of this amino acid can enhance enzyme activity. However, the consequences of its presence may vary, depending on the surrounding amino acids. For example, in some cases, its acidic nature may disrupt interactions with other residues. This can lead to decreased stability or altered function.
Additionally, glutamic acid is significant in neurotransmitter activity. In the brain, it serves as a neurotransmitter itself. Its interplay with other amino acids is complex and cannot be overlooked. While it promotes signaling, imbalances can lead to negative effects on cognitive function. Researchers continue to study these dynamics to better understand protein interactions and their implications.
Glutamic acid residue is pivotal in protein structure and function. It plays a critical role in drug design and therapeutics. This residue often acts as a key player in enzyme activity and receptor interactions. Its negative charge makes it an excellent candidate for ionic interactions. These characteristics can enhance drug effectiveness.
In drug development, understanding glutamic acid's role can lead to improved therapeutic outcomes. Researchers focus on modifying drug molecules to optimize interactions with glutamic acid residues. However, this process can be complex and unpredictable. Small changes in residue chemistry can yield significant fluctuations in drug efficacy.
The challenge lies in balancing potency with safety. Not all modifications will result in a favorable therapeutic profile. Each drug candidate requires rigorous testing to ensure it interacts appropriately with glutamic acid. Addressing these uncertainties is essential for successful drug development. The journey is not straightforward, yet the potential rewards are significant. Each step reveals new insights for future therapies.
Whether you’re a homeowner, builder, or designer, you’ll find that our elegant cabinets create a breathtaking space that evokes positive emotions and encourages lasting memories. We invite you to explore our website to learn more about who we are and how we can help you.
Woodinville | Bellevue | Seattle | Kirkland | California | Berkeley | Walnut Creek | Roseville, CA
© 2025 Acadia Craft. Powered by Integrity Marketing Serving Woodinville, Kirkland, Bellevue & The Greater Seattle Area
